What is Psychosis?
Psychosis is a mental health condition that affects how a person perceives reality. It often involves hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that aren’t there) and delusions (strong false beliefs that are not based on reality). People experiencing psychosis may struggle with thinking clearly, making decisions, or understanding what is real and what is not.
Symptoms of Psychosis
- Hallucinations – Hearing voices, seeing things, or feeling sensations that aren’t real.
- Delusions – Strong, false beliefs (e.g., believing someone is spying on them).
- Disorganized Thinking – Confused speech, jumping from one topic to another.
- Abnormal Behavior – Unusual or inappropriate actions, difficulty completing daily tasks.
- Lack of Insight – Not realizing that their thoughts or experiences are distorted.
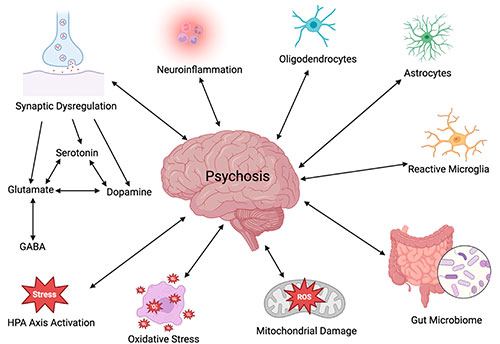
Causes & Risk Factors
Psychosis can be triggered by various factors, including
- Mental Health Disorders – Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder, Severe Depression
- Substance Use – Drugs like LSD, marijuana, or methamphetamine
- Medical Conditions – Brain injuries, infections, neurological disorders.
- Extreme Stress or Trauma – Sudden loss, abuse, or major life changes
Treatment for Psychosis
- Medication: Antipsychotic drugs help reduce symptoms by balancing brain chemicals.
- Psychotherapy: Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps individuals manage thoughts and emotions
- Hospitalization: In severe cases, hospitalization ensures safety and proper care
- Lifestyle & Support: Stress management, social support, and a structured routine aid in recovery
